Construction health and safety management system: Success strategies
by
Metam technologies

Abstract
This article provides a comprehensive guide to creating a Construction Health and Safety Management System (CHSMS) that minimizes accidents and maximizes productivity. It includes proven strategies, the latest industry trends, and practical tips for overcoming common implementation challenges. Learn how to design a system that not only meets regulatory standards but exceeds industry expectations.
Table of Content
What is a construction health and safety management system and why is it essential?

How to develop a robust construction health and safety management system?

What are the key success strategies to enhance a construction safety system?

What are the common pitfalls in implementing a construction health and safety management system and how can they be avoided?

Key takeaways

Imagine a construction site where every worker is not only safe but empowered by a system that anticipates risks before they occur. This proactive approach is becoming the industry standard for modern construction health and safety. According to recent OSHA data, companies that integrate comprehensive construction health and safety management systems have experienced a 20% reduction in workplace incidents.
A Construction Health and Safety Management System (CHSMS) is designed to reduce accidents, boost productivity, and ensure compliance with all regulatory standards. It’s more than just a set of rules – it’s a framework that anticipates and mitigates risks, empowering workers and driving operational success.
What is a construction health and safety management system and why is it essential?
A Construction Health and Safety Management System (CHSMS) plays a critical role in ensuring safety on construction sites. It encompasses policies, risk management, and compliance measures designed to minimize risks and improve overall productivity.
Definition
A Construction Health and Safety Management System (CHSMS) is a structured approach designed to ensure the health and safety of workers on construction sites. It integrates policies, risk management practices, and monitoring tools to proactively reduce accidents and ensure compliance with regulations. Unlike general safety programs, a CHSMS is holistic, encompassing all aspects of safety from risk assessment to incident reporting. By integrating these elements, CHSMS fosters a continuous improvement loop.
Core components
To create an effective CHSMS, it's essential to implement the following key components:
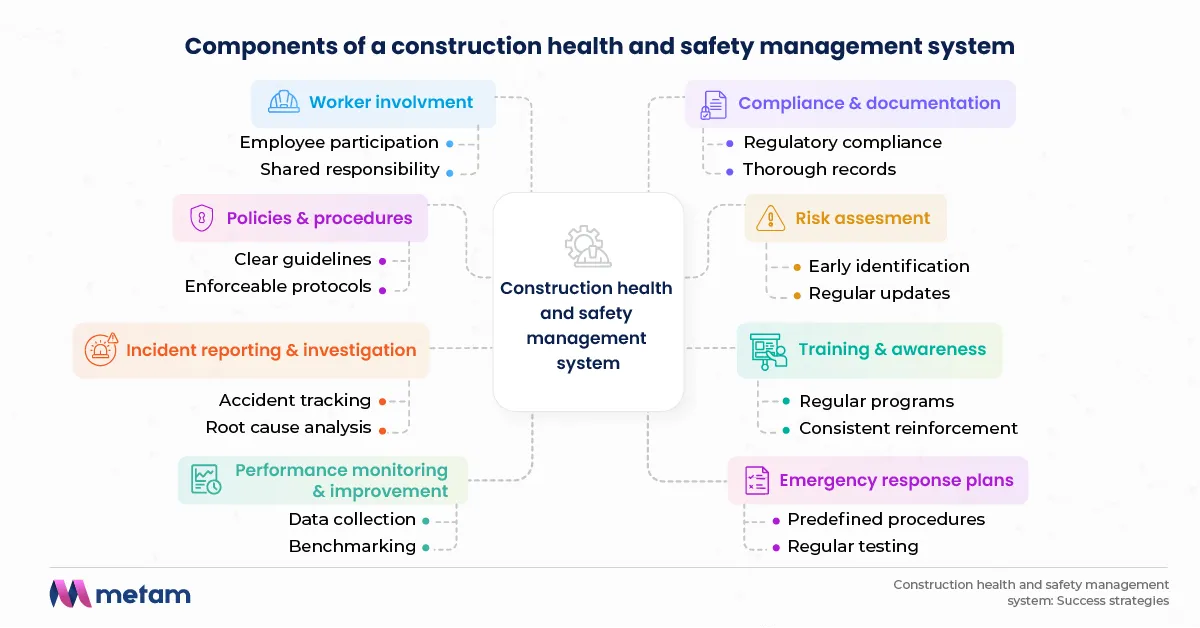
- Policies & procedures: Clear safety guidelines and expectations are the foundation of any successful CHSMS. These policies ensure that safety protocols are consistent, widely understood, and enforceable across all levels of the workforce.
- Risk assessment: Identifying hazards early on ensures mitigation strategies are in place to prevent accidents. Regular, updated risk assessments also help address new risks as construction methods and materials evolve.
- Training & awareness: Regular training programs equip workers with the knowledge and skills to handle potential risks. Consistent reinforcement ensures that safety remains a top priority throughout a worker's career.
- Incident reporting & investigation: Tracking accidents and near-misses helps identify systemic issues and fosters a learning culture. Thorough investigations uncover root causes, improving the system and preventing future incidents.
- Performance monitoring & improvement: Ongoing analysis and data collection drive continuous improvement. By benchmarking safety performance against industry standards, companies can ensure they remain competitive and compliant.
- Emergency response plans: Having predefined procedures ensures a swift and effective response to emergencies. These plans should be regularly tested and refined to adapt to new challenges on-site.
- Worker involvement: Encouraging employees to participate in safety initiatives promotes buy-in and reinforces safety as a shared responsibility. Workers who are part of the process are more likely to adhere to safety guidelines and suggest improvements.
- Compliance & documentation: Ensuring compliance with local regulations and maintaining thorough records is critical to legal and operational success. Keeping documentation up to date reduces legal risks and proves adherence to safety standards during audits.
Importance in the construction industry
The construction industry is inherently risky, with accidents leading to injuries, fatalities, legal liabilities, and project delays. A well-implemented CHSMS reduces these risks, enhances operational efficiency, and fosters a safety culture that improves worker morale. Moreover, OSHA compliance is a critical aspect of maintaining safety standards and avoiding costly penalties. A proactive approach to safety can dramatically reduce the financial impact of incidents.
Real-world examples of construction companies that successfully implemented CHSMS show measurable improvements in safety records, proving that a proactive approach to safety results in fewer incidents and greater productivity.
How to develop a robust construction health and safety management system?
Developing a robust Construction Health and Safety Management System involves careful planning and strategic implementation. By focusing on risk assessment, policy development, and integrating safety into existing project management systems, construction companies can create a culture of safety that lasts.
- Planning and risk assessment: A comprehensive risk assessment is the cornerstone of any safety system. Start by identifying potential hazards at each stage of the construction project, from design to execution. Utilize modern risk analysis tools to evaluate environmental, physical, and operational risks. Regularly update risk assessments to reflect evolving site conditions and new safety trends.
- Policy development and regulatory compliance: Develop policies that align with OSHA regulations and local safety standards. Ensure that safety protocols are not only compliant but also incorporate best practices and industry benchmarks. Regularly update these policies to reflect evolving standards and technologies. A strong policy foundation guarantees that safety is embedded in the project from the start.
- Training and implementation best practices: Safety training should be ongoing, with both initial and refresher courses. Ensure that the content is tailored to the specific needs of your workforce and construction site. Interactive, hands-on training methods enhance learning and retention, making workers more adept at identifying and responding to hazards on-site.
- Integration with existing project management systems: Integrate the safety management system with project management tools to streamline communication and ensure safety measures are incorporated into every aspect of the project. This helps create a seamless process where safety is prioritized alongside construction goals. Integration also provides a comprehensive view of project timelines, budgets, and potential risks.
- Digital tools and software for safety management: Leverage technology to monitor safety in real-time. Tools such as IoT sensors, mobile apps, and AI-powered software provide instant updates on site conditions, ensuring timely interventions when risks are identified. These tools also provide valuable data for ongoing safety assessments and audits.
- Creating a culture of safety: A culture of safety begins with leadership. Senior management must commit to prioritizing safety, leading by example, and fostering an environment where safety is everyone’s responsibility. Encourage open communication and empower workers to speak up about safety concerns, creating a workforce that feels responsible for their own and their colleagues' well-being.
- Continuous evaluation and improvement: The construction industry is dynamic, and so are the risks. Regularly evaluate the safety system through audits and feedback loops. Incorporate lessons learned from past incidents and refine processes to address emerging risks. Continuous evaluation ensures that the system remains relevant and effective in mitigating evolving threats.
What are the key success strategies to enhance a construction safety system?
The effectiveness of a construction health and safety system can be significantly enhanced by adopting innovative technologies, conducting regular audits, and fostering collaboration. These strategies contribute to a more responsive and agile safety framework that is adaptable to future challenges.
- Leveraging technology and innovation : The future of construction safety lies in technology. IoT devices can track worker movements and environmental conditions, while AI-powered tools predict and prevent potential accidents by analyzing historical data. Real-time monitoring systems can alert workers and managers about risks before they escalate into accidents, allowing for immediate corrective action.
- Regular audits and data-driven improvements : Consistent audits are essential for identifying areas of improvement. Use data from past incidents, near-misses, and safety reports to drive enhancements. KPIs, such as incident frequency rates and response times, should be tracked and analyzed to inform decision-making. Data-driven decisions allow for targeted improvements that directly reduce risks.
- Collaboration with external safety consultants : Bringing in external experts to audit and assess your safety systems can provide an unbiased perspective. Safety consultants can identify gaps in the current system and recommend tailored solutions to improve safety performance. Their expertise ensures that the safety system remains effective and compliant with the latest regulations.
- Gamification in safety training : Gamification introduces an interactive element to safety training, increasing engagement and retention. By turning safety protocols into challenges or simulations, workers are more likely to absorb key concepts and apply them in real-world scenarios. This makes learning fun, memorable, and more likely to translate into safer behavior on-site.
- Engaging workers in safety leadership : When workers take an active role in safety leadership, they are more committed to maintaining a safe work environment. Encourage employees to lead safety meetings, identify hazards, and propose solutions. Empowering workers fosters a sense of ownership and accountability for site-wide safety initiatives.
- Managing safety across multiple sites : Consistency is key when managing safety on multiple construction sites. Standardize safety protocols and ensure all workers are trained to the same high standard. Utilize software that tracks safety data across sites for easier monitoring and compliance. This streamlines the safety management process and ensures no site is left behind in maintaining high safety standards.
What are the common pitfalls in implementing a construction health and safety management system and how can they be avoided?
Implementing a CHSMS can present several challenges, from resource allocation to leadership commitment. Identifying and addressing these potential pitfalls early on is crucial to ensuring the system’s success.
- Identifying and addressing gaps: Common mistakes include failing to properly assess risks or underestimating the complexity of implementing a CHSMS. Ensure thorough planning and involve all stakeholders early in the process to identify and address potential gaps. This proactive approach prevents costly oversights that can compromise safety.
- Budget and resource allocation challenges: Safety systems can be costly, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment. Allocate sufficient resources for training, technology, and safety equipment. Prioritize safety expenditures to avoid unforeseen costs down the line, ensuring that every worker has the tools and knowledge to work safely.
- Best practices from industry leaders: Companies like Bechtel have navigated these challenges by adopting innovative safety solutions, maintaining strong leadership commitment, and continuously improving their safety programs. By learning from their experience, others can avoid common pitfalls. These companies demonstrate how investment in safety systems translates to reduced incidents and greater worker satisfaction.
- Overlooking worker involvement: Failing to involve workers in the development and implementation of safety protocols can lead to disengagement. Ensure that workers feel heard and valued in the safety process. When workers are part of the decision-making process, they are more likely to adhere to safety measures and take ownership of site safety.
- Inadequate emergency response planning: Inadequate emergency response plans can have catastrophic consequences. Regular drills, clear communication, and effective resources are key to ensuring that workers can respond effectively during an emergency. A well-rehearsed emergency plan saves lives and reduces the chaos during an actual emergency.
- Failing to update systems with new regulations: Regulations are constantly evolving, and so should your safety system. Stay up to date with new OSHA guidelines and industry standards to maintain compliance and reduce risk. Regularly reviewing and updating safety protocols ensures that your system stays current and compliant, reducing the likelihood of legal issues.
- Lack of leadership commitment: Without senior leadership buy-in, a CHSMS is unlikely to succeed. Ensure that executives lead by example, allocate resources, and foster a culture where safety is always the top priority. Strong leadership commitment is essential to creating a safety-first environment where all team members prioritize health and safety.
Key takeaways
A construction Health and Safety Management System is a vital framework for reducing accidents, boosting productivity, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Its successful implementation hinges on strong leadership, comprehensive risk assessments, and continuous improvement through feedback and audits.
By integrating innovative technologies and involving workers in safety leadership, construction companies can create a safety-first culture that leads to long-term success. Maintaining an agile safety system that adapts to new risks and evolving regulations ensures a safer, more productive work environment.

Construction compliance...
This article explores the transformative role of compliance automation in construction health and safety management,...




