Health and safety in construction and engineering are crucial for legal compliance and worker protection. This guide explores essential safety management components, risk mitigation strategies, and the role of technology in enhancing workplace safety.
Ensuring robust health and safety management in construction and engineering is both a legal obligation and a moral imperative. Professionals in these industries face the challenge of navigating complex regulations, managing diverse teams, and mitigating numerous risks to maintain safe working environments.
According to a 2025 report by the National Safety Council (NSC), companies with strong safety management systems experience significantly fewer workplace accidents than those without.
This article provides essential insights into the key components of health and safety management, offering practical guidance to help professionals improve safety protocols and cultivate a culture of safety within their projects.
Understanding the fundamental elements of a comprehensive health and safety management system is essential for professionals aiming to either implement or enhance safety protocols within their organizations.
A robust health and safety management system starts with the commitment of management and leadership. This involves establishing clear safety policies that reflect the organization’s dedication to health and safety. These policies should be communicated effectively across the organization and incorporated into daily operations. Leadership must also actively participate in safety meetings and set an example by modeling safe behaviors themselves. When leaders demonstrate a strong commitment to safety, it encourages all team members to prioritize safety and adhere to the established protocols.
A key element of an effective safety management system is the identification of potential hazards and the implementation of comprehensive risk assessment procedures. Regular site inspections are critical for identifying hazards and assessing risks on the ground. These inspections should be systematic and thorough, with a focus on identifying both obvious and hidden risks. After identifying these hazards, it is crucial to implement standardized procedures that assess and prioritize the risks. By doing so, construction and engineering professionals can proactively address the most critical safety concerns and minimize the likelihood of accidents.
Ensuring the competence of workers is another essential aspect of health and safety management. Providing ongoing training programs is vital to ensure that all workers are well-versed in safety practices and know how to respond in emergencies. These programs should cover a wide range of safety protocols, from basic protective measures to emergency response procedures. In addition, ensuring that workers have the necessary certifications and licenses for their specific roles is a key part of maintaining safety. This ensures that workers are not only informed but also capable of effectively managing safety risks.
Effective communication and consultation are foundational to a successful safety management system. Regular safety meetings are essential for discussing concerns, sharing updates, and reinforcing safety practices. These meetings provide an opportunity for workers to voice their concerns and contribute to safety discussions. Additionally, establishing clear feedback mechanisms allows workers to report hazards or suggest improvements. This two-way communication fosters a culture of transparency and collaboration, ensuring that safety concerns are promptly addressed.
Planning for emergencies is an integral part of health and safety management. Developing and communicating comprehensive emergency response plans for various scenarios is essential for ensuring the safety of all personnel. These plans should be regularly updated and include clear procedures for evacuation, first aid, and crisis management. Moreover, conducting drills and simulations is crucial to ensuring that workers are familiar with emergency procedures and can respond quickly and efficiently in case of an actual emergency.
Monitoring safety performance is essential for ensuring the continued effectiveness of safety measures. Regular safety audits should be conducted to assess whether the current safety protocols are being followed and whether they are yielding the desired results. These audits provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of safety measures and highlight areas that need improvement. Using audit findings to drive continuous improvement ensures that safety protocols are always evolving to address new risks and challenges.
As professionals begin to understand the key components of an effective health and safety management system, it is also crucial to explore how modern technology can play a pivotal role in enhancing safety protocols and outcomes.
Modern technology offers innovative tools and solutions that can significantly enhance safety in construction and engineering projects. By leveraging advanced technology, professionals can reduce human error, predict risks, and create more efficient safety systems.
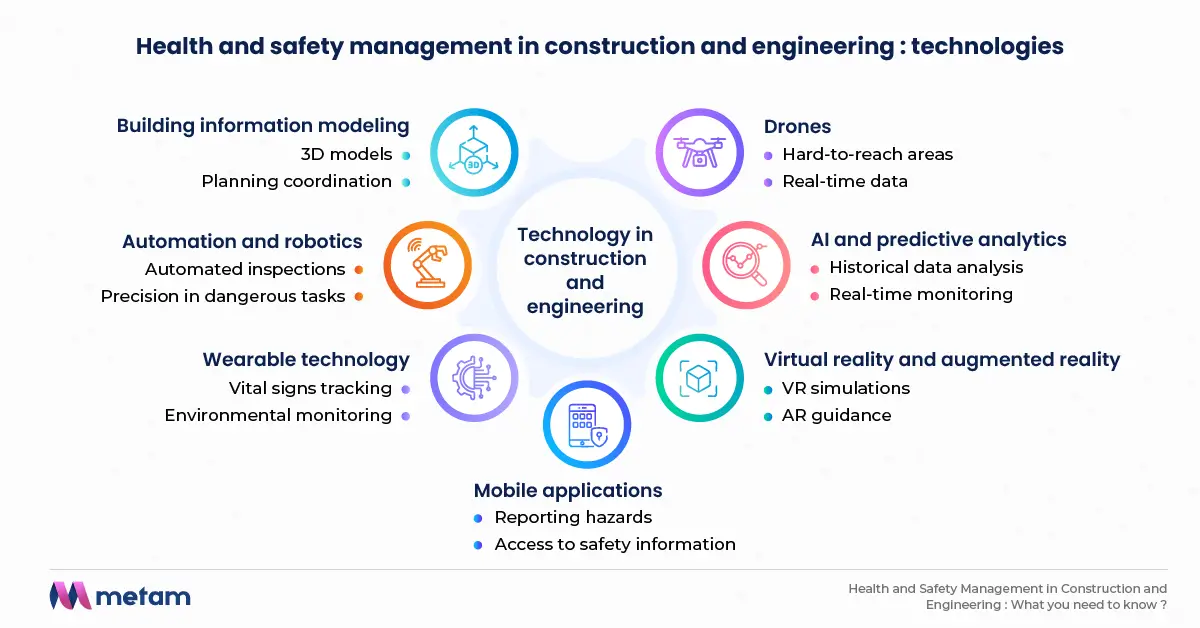
While technology plays a crucial role in enhancing safety, it is equally important for professionals to understand their legal responsibilities in maintaining health and safety standards.
Legal responsibilities play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and avoiding legal repercussions. Professionals must be aware of their duties under relevant regulations and laws to create a safe and compliant working environment.
Professionals in construction and engineering have a duty of care to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of their employees and others affected by their work activities. Employers are responsible for providing a safe working environment, adequate training, and the necessary protective equipment. Employees, in turn, have a responsibility to take reasonable care for their own safety and the safety of others, adhering to safety protocols and reporting potential hazards.
Compliance with health and safety regulations is non-negotiable. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace safety, including specific guidelines for construction sites. In the United Kingdom, professionals must comply with the Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 (CDM Regulations), which outline safety duties for all parties involved in a construction project. Ensuring compliance with these regulations helps prevent accidents and legal liabilities.
Accurate reporting and documentation are essential for maintaining safety standards. Certain incidents must be reported to relevant authorities within specific timeframes, and maintaining thorough records of risk assessments, training sessions, and safety audits is crucial. These records not only help in demonstrating compliance but also provide valuable insights for improving safety protocols in the future.
Failure to comply with health and safety regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal action. In addition to financial consequences, non-compliance can damage a company's reputation, leading to lost business opportunities and a lack of trust from clients and stakeholders.
Recognizing legal obligations and adhering to safety regulations is crucial for ensuring compliance and fostering a culture of safety within the workplace. Moving forward, identifying and mitigating common safety hazards is critical for maintaining a safe work environment.
A strong safety culture is essential for reducing workplace accidents and ensuring long-term compliance with safety regulations. In construction and engineering, fostering such a culture involves several key practices that encourage proactive safety behaviors and shared responsibility.
Incorporating these practices into everyday operations fosters a strong safety culture that minimizes risks and ensures a safer working environment for everyone.
At Metam Technologies, the importance of health and safety in construction and engineering is deeply understood. That’s why we provide advanced, tailored digital solutions designed to not only meet but exceed industry safety standards.
By leveraging Metam’s innovative technologies, organizations can stay ahead of evolving safety regulations, optimize their operations, and foster safer, more efficient work environments. Our customized solutions seamlessly integrate cutting-edge tools, empowering teams to enhance safety protocols, stay compliant with regulations, and significantly improve overall project safety and productivity.
Health and safety management in construction and engineering is a complex, multifaceted process that demands strong leadership, proactive hazard identification, and ongoing employee training.
By fully understanding legal responsibilities and adopting innovative safety solutions, professionals can create safer work environments, reduce risks, and enhance project outcomes. Prioritizing health and safety not only protects workers but also drives improved productivity, operational efficiency, and long-term project success.


